Crypto Market Cycles Explained
Bitcoin and Crypto Market Cycles Explained
Key Takeaways
- Crypto market cycles follow a recurring pattern of four phases: Accumulation, Markup, Distribution, and Markdown.
- Understanding these phases can help you make more informed and strategic investment decisions.
- External factors like Bitcoin halvings, major news events, and regulatory changes often influence the timing and intensity of each cycle.
- While crypto cycles can be shorter and more volatile than traditional markets, historical patterns, especially around Bitcoin’s 4-year halving schedule, offer useful insights.
The crypto market is exciting, fast-moving, and often volatile. But despite its reputation for unpredictability, there’s some rhythm to the chaos. Over time, Bitcoin and broader crypto markets tend to move in recurring patterns - known as crypto market cycles.
Understanding these cycles is essential for anyone looking to make smarter investment decisions. In this guide, we’ll break down the four key phases of a typical crypto market cycle and the factors that influence them - so you can navigate the market with greater confidence.
What are Bitcoin and Crypto Market Cycles?
Market cycles refer to the recurring stages of price movement seen across the digital asset market over time. These patterns mirror those in traditional markets - periods of growth followed by corrections or declines - but tend to be faster and more volatile.
Driven by a mix of market psychology, investor sentiment, supply-demand dynamics, and external events, these cycles form the foundation of how crypto prices move over months and years.
Think of a market cycle as a blueprint showing the emotional and financial journey from market lows to highs and back again. For investors, recognising these stages can help identify opportunities - and avoid costly mistakes.
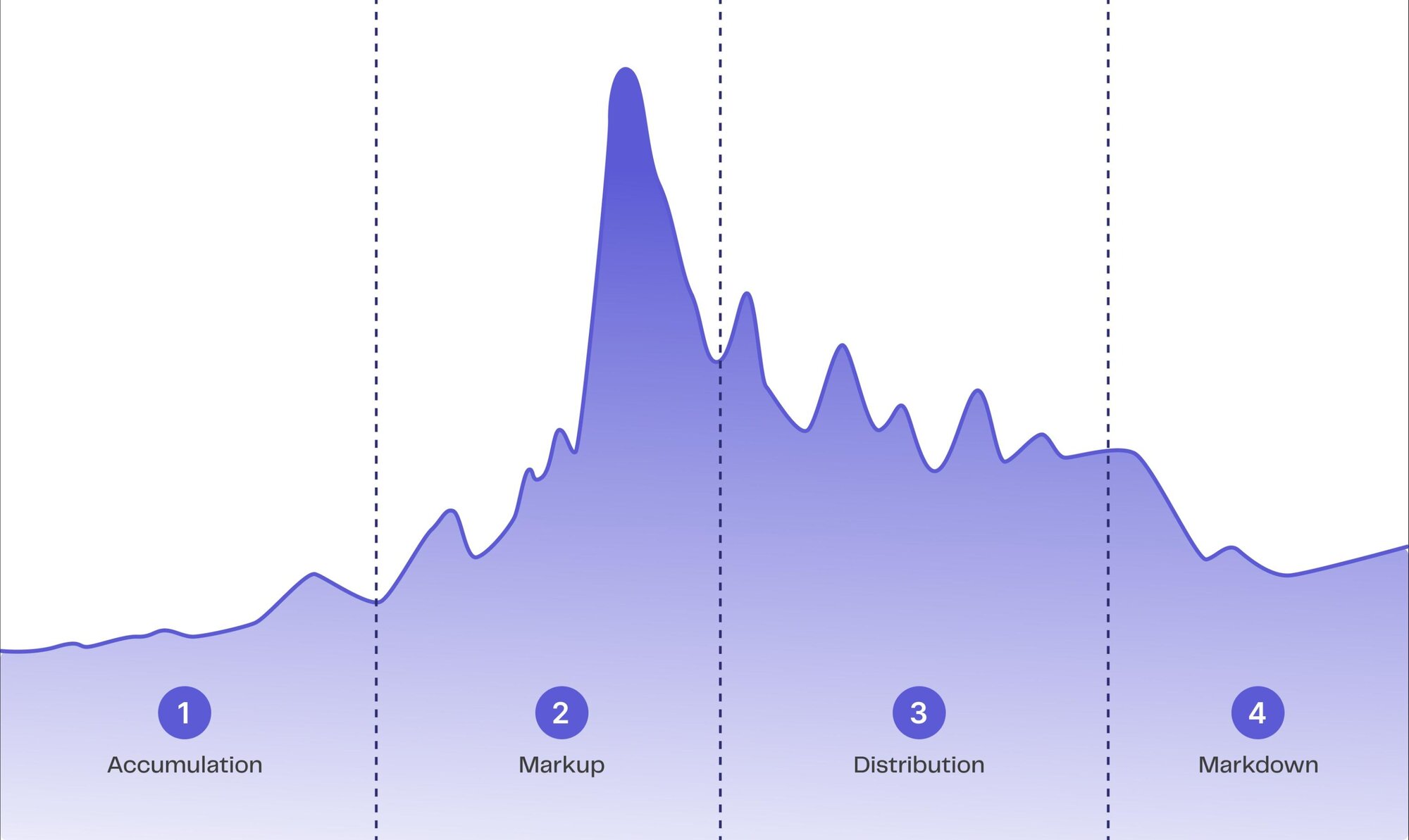
The Four Phases of a Crypto Market Cycle
Each market cycle typically includes four main phases: Accumulation, Markup, Distribution, and Markdown. Let’s explore what happens during each phase.
1) Accumulation Phase
Accumulation marks the beginning of every market cycle. Following the end of the previous cycle after a sharp rise and dramatic fall in prices, long-term investors and institutions start to accumulate undervalued cryptocurrencies, believing that the market has bottomed out.
Characteristics:
- Prices are stable and range-bound
- Market sentiment shifts from fear to cautious optimism
- Trading volume is low
- Little media coverage or public interest
This phase is also known as “consolidation.” It’s often the best time to accumulate crypto, but it requires patience and discipline.
Recommended Reading: Crypto Dollar Cost Averaging Explained
2) Growth and Bull Market Phase
As the Accumulation Phase ends, the Markup Phase begins, marked by a significant increase in market interest and positive sentiment. New traders and investors enter the market, driving up demand, asset prices, and trading volumes. Market conditions improve with a sustained positive trend, often fuelled by media hype, increased public awareness, and a fear of missing out (FOMO) among retail investors. This stage is commonly deemed as the start of the bull market or bull run.
Characteristics:
- Trading volume increases
- Prices make higher highs
- Positive media coverage fuels interest
- Demand outweighs supply
This stage is commonly known as the start of a bull run. While the overall trend is up, expect corrections and volatile fluctuations along the way.
Recommended Reading: Bull vs Bear Market: What’s the difference?
3) Distribution Phase
The Distribution Phase commences as the market reaches its peak, with bulls and bears battling for dominance. Although trading volume remains high, asset prices fluctuate within a tight trading range until one side concedes. Market sentiment transitions from optimism to mixed emotions, driven by fear, greed, and hope.
Towards the end of this phase, the market will move in the opposite direction. This can take weeks or several months to play out, but typically the higher the extreme highs, the quicker the pieces fall. Investors who missed selling earlier at a profit now settle to break even - or take a slight loss.
Characteristics:
- Trading volume remains high
- Prices move within a tight range
- Sentiment becomes mixed - greed, fear, and hope collide
- Signs of exhaustion and volatility appear
This phase often ends with a sharp reversal, usually leading into a bear market.
Recommended Reading: Crypto Fear and Greed Index Explained
4) Markdown and Bear Market Phase
The fourth and final phase of market cycle's is the Markdown Phase, also known as the bear market. As supply exceeds demand, upward market momentum slows down, buying interest dries up, and no new capital enters the market. Selling pressure builds, and fear fuels the market, leading to a sharp decline in prices, hence the name Markdown.
With red the candle colour of the day, many new investors exit the market or become forced sellers. Panic selling frequently takes hold, potentially triggering a domino effect of plummeting prices across all assets. In certain instances, this may drive asset values down to points not witnessed since the Markup Phase. Numerous investors may face considerable losses, as the market experiences a notable decline in trading volume as participants opt to bide their time on the sidelines.
Characteristics:
- Prices trend downward
- Supply outweighs demand
- Price volatility Increases
- Trading volume declines
- Market sentiment turns bearish
For those who remain patient and vigilant, the Markdown Phase can offer opportunities to accumulate cryptocurrencies at discounted prices, preparing for the next Accumulation Phase and the start of a new cycle.
Factors That Affect a Cryptocurrency Market Cycle
Several factors can shape the direction and length of a crypto market cycle. Key influences include:
Bitcoin Halvings
Every four years, the issuance rate of new Bitcoin (BTC) is cut in half in an event known as “the Bitcoin Halving”. With a reduction in supply, demand for BTC can increase, which generally pushes the price of BTC higher. As the market's leading asset, when Bitcoin's price rises, most other asset prices tend to increase too. Historically, Bitcoin's Halvings have coincided with a new markup phase, making it a good indicator to pay attention to.
Major Crypto News
Events like exchange hacks, protocol failures, or groundbreaking product launches can create sharp shifts in investor sentiment and market direction. Notable recent events such as Terra (LUNA) imploding or the FTX debacle have all had lasting ripple effects across the crypto industry.
Regulation and Policy Changes
Government policies and regulations related to cryptocurrencies and crypto trading, such as taxation, security measures, or bans, can significantly influence market cycles by either encouraging or discouraging investor participation.
Social Media Sentiment
Social media platforms like X (formerly Twitter), Telegram, and Discord have become major hubs in the crypto community. Trends and narratives often begin here before spilling into broader markets.
How Long Does a Crypto Cycle Last?
Crypto market cycles vary in length, ranging from several months to a few years. Historically, many believe Bitcoin operates on a four-year cycle, influenced by its halving schedule.
For example:
- 2013: BTC rose from US$150 to over US$1,150, then fell to US$250 by 2015
- 2017: BTC surged from US$1,000 to US$19,000, before dropping to ~US$3,700
- 2020–2021: After the 2020 halving, BTC hit ~US$69,000 before entering a new markdown
Observing these patterns, some investors subscribe to the "four-year cycle theory." This idea proposes that a major markup phase occurs a few months after Bitcoin's supply is halved every four years. Where crypto assets then reach unsustainable peaks before their prices drop and stabilise close to the previous cycle's highs. They remain in this accumulation phase until the next Bitcoin halving.
It's important to note that while past trends suggest a pattern, nothing is guaranteed. Black swan events, regulatory shifts, and market maturity can all influence future cycles.
Investment Considerations
While no one can predict the market perfectly, understanding crypto market cycles can help you:
- Recognise buying and selling opportunities
- Stay calm during volatility
- Avoid emotional investment decisions
The key is to stay informed, plan ahead, and avoid chasing hype.
FAQs
How long do crypto cycles last?
What causes crypto market cycles?
Does crypto follow a 4-year cycle?
Disclaimer: This article and its contents are intended for informational purposes only, and do not constitute financial, investment, trading or any other advice from TWMT Pty Ltd, trading as Coinstash AU ("Coinstash"). Coinstash is not a licensed financial advisor and does not provide financial advice. You should not make any decision, financial, investment, trading or otherwise, based on any of the information presented in this webinar or relevant materials without undertaking independent due diligence and consultation with a professional financial adviser. The information presented in this article may be inaccurate and no representations are made as to its truthfulness or accuracy. The views and opinions expressed in the quoted material are those of the original authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of Coinstash. All quotes have been used for informational purposes and have been attributed to their respective sources to the best of our ability.You understand that you are using any and all information available in or through this webinar or relevant materials at your own risk. Cryptocurrency is a highly volatile and risky investment. You should consider seeking financial, legal, tax or other professional advice to check how the information relates to your unique circumstances. Coinstash shall not be held responsible or liable for any losses, whether due to negligence or otherwise, stemming from the use of, or reliance upon, the information provided directly or indirectly in this article.
Contents
Key Takeaways
What are Bitcoin and Crypto Market Cycles?
The Four Phases of a Crypto Market Cycle
1) Accumulation Phase
2) Growth and Bull Market Phase
3) Distribution Phase
4) Markdown and Bear Market Phase
Factors That Affect a Cryptocurrency Market Cycle
How Long Does a Crypto Cycle Last?
Investment Considerations
FAQs